38 longitudinal wave labled
Longitudinal wave - Labelled diagram - Wordwall Longitudinal wave. Share Share by Misshutchinson. KS4 Physics Science. Show More. Like. Edit Content. Embed. More. Leaderboard. Show more Show less . This leaderboard is currently private. Click Share to make it public. This leaderboard has been disabled by the resource owner. This leaderboard is disabled as your options are different to the ... Longitudinal and Transverse Wave Motion - Pennsylvania State University Water waves are an example of waves that involve a combination of both longitudinal and transverse motions. As a wave travels through the waver, the particles travel in clockwise circles. The radius of the circles decreases as the depth into the water increases. The animation at right shows a water wave travelling from left to right in a region ...
Longitudinal Wave Examples, Parts & Diagram | Amplitude of a ... Sound waves, as all examples of longitudinal waves, require a material for it to propagate. The amplitude of a sound wave is related to its loudness. The larger the amplitude, the louder the sound.
Longitudinal wave labled
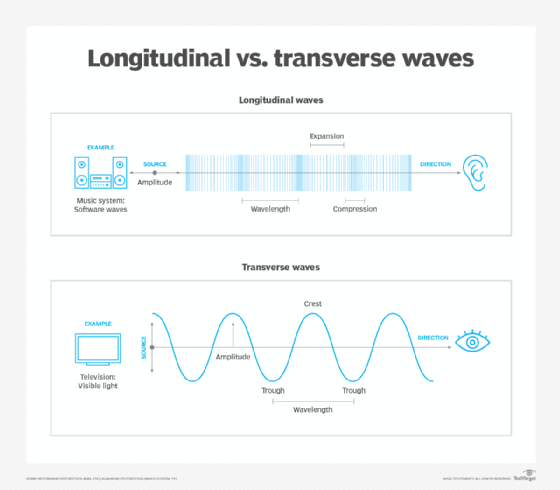
Label & Draw Transersve Waves: Amplitude, Frequency ... - YouTube Learn how to QUICKLY label a transverse wave with crest, trough, wavelength, frequency, amplitude, resting position and resting points. We will also learn h... Longitudinal waves - Properties of waves - Eduqas - BBC Bitesize Waves transfer energy but not matter. Waves may be transverse (eg water wave) or longitudinal (eg sound wave). Wave motion can be described using the terms amplitude, wavelength, frequency and period. 9.3 Wavelength and amplitude | Longitudinal waves | Siyavula For a longitudinal wave which is a pressure wave this would be the maximum increase (or decrease) in pressure from the equilibrium pressure that is cause when a compression (or rarefaction) passes a point. Figure 9.3: Wavelength of a longitudinal wave. The amplitude is the distance from the equilibrium position of the medium to a compression or ...
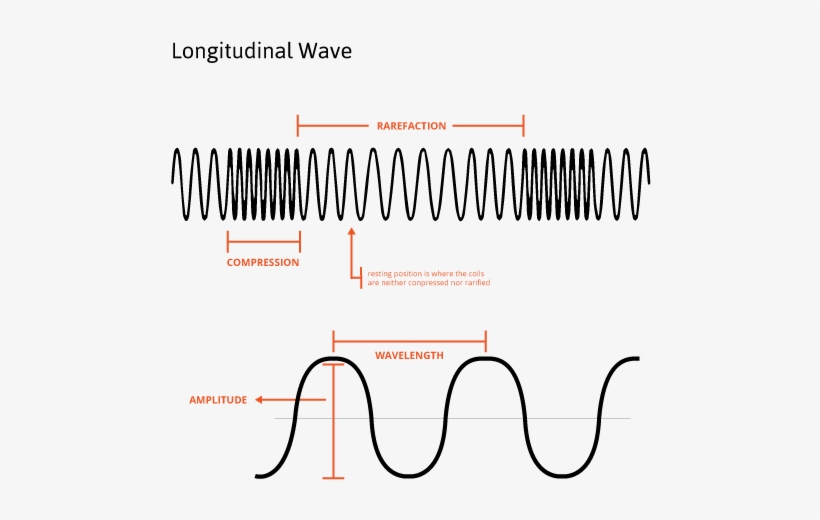
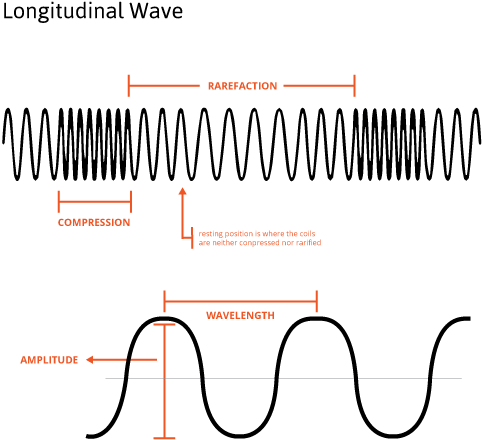
Longitudinal wave labled. 9 Best Examples Of Longitudinal Waves In Everyday Life Figure 1. A simple example of such waves is compressions moving along a slinky. One can generate a longitudinal wave by pushing and pulling the slinky horizontally. When traveling through a medium, these waves create compression and rarefaction. Compressions are high-pressure regions where wave particles are close together. Longitudinal Wave - Explanation, Examples and FAQs - VEDANTU The longitudinal waves are mechanical waves and these are readily used in nature for transmitting energy from one point to another within the medium. There are several examples of longitudinal waves. Sound waves are the most common example of longitudinal waves, pressure waves, spring waves, etc…. Let's have a look at these examples in ... Longitudinal waves - Transverse and longitudinal waves - AQA - GCSE ... Longitudinal waves are often demonstrated by pushing and pulling a stretched slinky spring. In the diagram, the compressions move from left to right and energy is transferred from left to right. ... How do you draw a longitudinal wave and label the parts ... - Answers How do you draw a longitudinal wave and label the parts? Wiki User. ∙ 2010-04-25 15:55:52. Study now. Best Answer. Copy. Just had this lesson this afternoon, 06.23.2009. Longitudinal ...
Longitudinal Waves and Labelling wave diagrams - YouTube Tutorial video on longitudinal waves, examples of these waves and how to label distinguishing features on three different types of wave diagram.This video an... Longitudinal Wave Label Diagram | Quizlet morgan_sanders25. AST 1002 Final Exam 2019. 60 terms. isabellarl515. Psychology Midterm 1b. 37 terms. tanyaaakay. Upgrade to remove ads. Only $35.99/year. Transverse & Longitudinal Waves Definition & Examples - BYJUS Transverse Waves And Longitudinal Waves. In Physics, waves are explained as an oscillation about the fixed point, accompanied by the transfer of energy travelling from one medium to another. When energy transfer occurs through a medium due to oscillation, the resultant wave can be termed a mechanical wave. The medium of transmission limits the ... Longitudinal wave - Wikipedia Longitudinal waves are waves in which the vibration of the medium is parallel ("along") to the direction the wave travels and displacement of the medium is in the same (or opposite) direction of the wave propagation. Mechanical longitudinal waves are also called compressional or compression waves, because they produce compression and rarefaction when traveling through a medium, and pressure ...
Longitudinal wave Definition & Meaning - Merriam-Webster a wave (such as a sound wave) in which the particles of the medium vibrate in the direction of the line of advance of the wave… See the full definition SINCE 1828 Longitudinal Wave: Definition, Parts & Examples - Study.com A longitudinal wave is a wave in which the disturbance moves in the same direction as the propagation of the wave. Going back to the Slinky example, the medium is the slinky, and the disturbance ... Draw a longitudinal wave and label the following properties:... Longitudinal wave. Sound is only a wave, whereas light exhibits both wave and particle properties. - Sound is a longitudinal wave, but light is a transverse wave. - Sound needs a material medium to travel, light can propagate through vacuum also. - Light travels much faster than the sound. 1 Attachment. jpg. Longitudinal wave- label Diagram | Quizlet Start studying Longitudinal wave- label. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
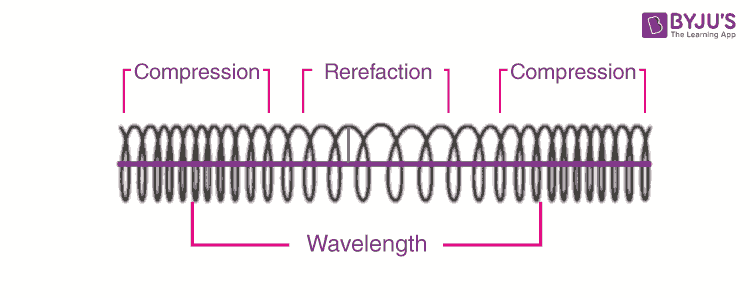
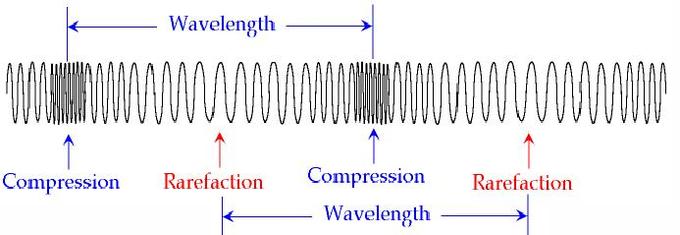
9.2 Compression and rarefaction | Longitudinal waves | Siyavula A rarefaction is a region in a longitudinal wave where the particles are furthest apart. As seen in Figure 9.2, there are regions where the medium is compressed and other regions where the medium is spread out in a longitudinal wave. The region where the medium is compressed is known as a compression and the region where the medium is spread ...
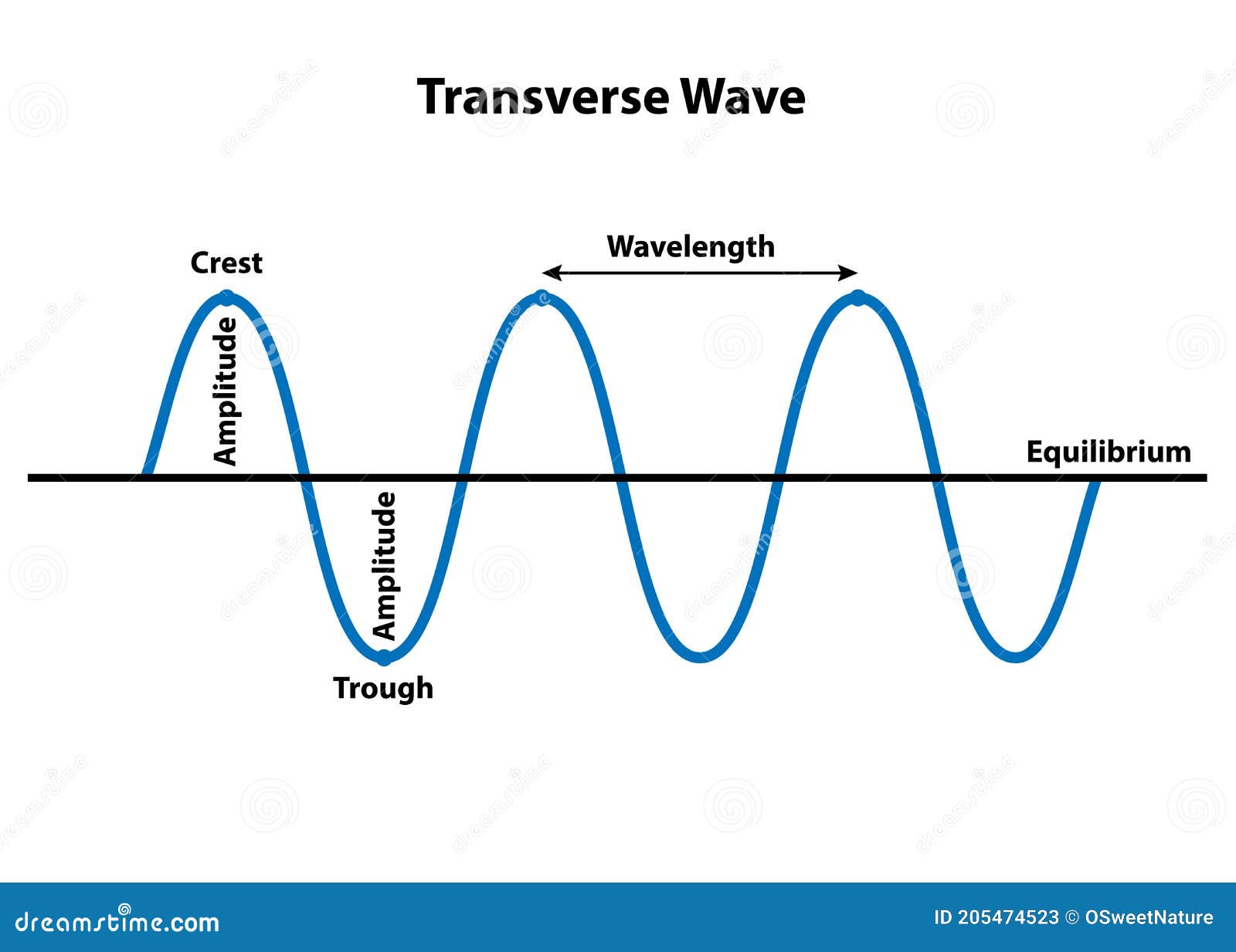
Parts And Types of A Wave - The Science Of Waves The wavelength of a transverse wave is the spatial period, or space, of the wave; the distance over which the wave's shape repeats. So basically like crest to crest. There are two types of waves; Transverse and Longitudinal or Compression Waves. Longitudinal Waves have different parts, however. The part of a longitudinal wave is called ...
Longitudinal Wave Label Lesson Plans & Worksheets For Students 9th - 12th. In this color worksheet, students answer 16 questions about light, color and wavelength. They label a graph of position vs. displacement and answer questions about the graph including finding the frequency, amplitude, and wavelength. +.
Longitudinal Wave - Definition, Examples, Formula, Diagram - BYJUS A wave that moves in the direction perpendicular to its propagation. A sound wave is an example of a longitudinal wave. Water waves are an example of a transverse wave. It is made of refractions and compressions. It is made of troughs and crests. This wave can be produced in any medium such as gas, liquid or solid.
7 Real Life Examples Of Longitudinal Waves - StudiousGuy 1. Speaking on the mic. A sound wave is a significant example of a longitudinal wave. When a speaker speaks some words in front of the microphone, he/she hit the air thousands of time per second at different frequencies. The sound particles travel along with the air particles and enter the mic to produce sound. 2.
longitudinal wave | physics | Britannica longitudinal wave, wave consisting of a periodic disturbance or vibration that takes place in the same direction as the advance of the wave. A coiled spring that is compressed at one end and then released experiences a wave of compression that travels its length, followed by a stretching; a point on any coil of the spring will move with the wave and return along the same path, passing through ...
Longitudinal Wave - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics The case of a wave in a fluid incident on a solid (Figure 3.12) is now treated in more detail in terms of an equivalent circuit.This problem is translated into the equivalent circuit representation of Figure 3.13A, which shows mode conversion from the incoming longitudinal wave into a longitudinal wave and a vertical shear wave in the solid.Since the motions of these waves all lie in the xz ...
Physics Tutorial: Longitudinal Sound Wave - Physics Classroom For a sound wave traveling through air, the vibrations of the particles are best described as longitudinal. Longitudinal waves are waves in which the motion of the individual particles of the medium is in a direction that is parallel to the direction of energy transport. A longitudinal wave can be created in a slinky if the slinky is stretched ...
Parts of Longitudinal and Transverse Waves Parts of waves. Parts of a Transverse wave: The crest is the top of the wave. The trough is at the bottom of the wave. The wavelength is the length of the wave. The amplitude of a wave is the highest amount of vibration that the medium gives from the rest position. The rest position is the position where a wave would be if there was no movement.
GCSE PHYSICS - What is a Longitudinal Wave? - GCSE SCIENCE Waves. What is a Longitudinal Wave?. When a longitudinal wave moves through a material, the particles of the material move backwards and forwards along the direction in which the wave is travelling. Below is a picture of a longitudinal wave travelling along a spring.. What is the Wavelength of a Longitudinal Wave?. The wavelength of a longitudinal wave can be measured
PDF Longitudinal waves - Harvard University However, for a longitudinal wave, ˆ is the longitudinal displacement, so although Fig. 1 is a perfectly valid plot of ˆ, it does not indicate what the wave actually looks like. There is no transverse motion, so the system simply lies along a straight line. What changes is the density along the line. You could therefore draw the wave by ...
9.3 Wavelength and amplitude | Longitudinal waves | Siyavula For a longitudinal wave which is a pressure wave this would be the maximum increase (or decrease) in pressure from the equilibrium pressure that is cause when a compression (or rarefaction) passes a point. Figure 9.3: Wavelength of a longitudinal wave. The amplitude is the distance from the equilibrium position of the medium to a compression or ...
Longitudinal waves - Properties of waves - Eduqas - BBC Bitesize Waves transfer energy but not matter. Waves may be transverse (eg water wave) or longitudinal (eg sound wave). Wave motion can be described using the terms amplitude, wavelength, frequency and period.
Label & Draw Transersve Waves: Amplitude, Frequency ... - YouTube Learn how to QUICKLY label a transverse wave with crest, trough, wavelength, frequency, amplitude, resting position and resting points. We will also learn h...




























Komentar
Posting Komentar